
70 | The Brave New (Quantum) World
Major advances across all the design stack of Quantum computing – algorithm, software, and hardware – has brought us to a realm where, it is impossible to ignore the effect of Quantum computing in the world around us.

68 | Bridging Hardware and Software: Optimizing Quantum Compilation and Benchmarking for Scalable Quantum Systems
This lecture discusses how integrated hardware–software co-design can address key challenges in scalable quantum computing.

67 | Quantum Recursive Programming: Verification and Implementation
Quantum recursive programming has recently been introduced for describing sophisticated and complicated quantum algorithms in a compact and elegant way.

64 | Decoder for quantum error correction codes: from the perspective of classical error correction codes
Quantum error correction has become a crucial and popular topic, especially given its essential role in ensuring the scalability and reliability of quantum computers.

69 | TQEC Tool Overview
Compiling a quantum algorithm to run on a quantum computer consisting of a 2D array of qubits with only nearest neighbor interactions is a complex problem.

59 | Achieve Explanable Quantum Computing Using Visualization
Quantum computing has made significant progress in recent years.

57 | Numerical Quantum Control: Scalable Gate Design and Calibration
The goal of numerical quantum control is to automate the gate design process, with the promise of rapid and flexible gate design for arbitrary systems.

58 | Variational Quantum Semi-definite Programming
Solving optimization problems is a key task for which quantum computers could possibly provide a speedup over the best known classical algorithms.

56 | ODEgen: Analytic Gradients of Quantum Pulse Programs
We introduce ODEgen, a new method for evaluating analytic gradients of quantum pulse programs and contrast it with the stochastic parameter-shift rule.

55 | Scaling Quantum Computing Systems via Codesign
The full promise of quantum computation will only be realized if quantum devices scale.

53 | Quantum Computational Chemistry: Variational Quantum Eigensolver and the Design of Ansatz
Over the past decade, quantum computing has experienced remarkable growth and development, opening up new possibilities for simulating molecular properties.

54 | Quantum Computing Systems: Challenges and Opportunities
The second quantum revolution, the transition from quantum theory to quantum engineering, is leading us toward practical quantum computing.

52 | Open Quantum Systems in Quantum Computing
Quantum dynamics in real-world scenarios seldom stand alone; they occur under the continuous influence of surrounding environments.

51 | Design Automation for Quantum Computing
This talk will provide the full picture of design automation for quantum computing - from designing quantum algorithms and quantum circuits to quantum computing using physical quantum hardware.
49 | Quantum Reservoir Engineering for Fast and Scalable Entanglement Stabilization
High-fidelity entanglement is a prerequisite for almost any quantum information processing task.

42 | Align or Not Align? Design Quantum Approximate Operator Ansatz (QAOA) with Applications in Constrained Optimization
Combinatorial optimization has been one of most promising use cases of the near-term quantum computers.

43 | A Structured Method for Compilation of QAOA Circuits in Quantum Computing
Zheng (Eddy) Zhang is an Associate Professor at Rutgers University.

46 | Numerical Methods of Optimal Quantum Control
At the heart of the next-level quantum technology like quantum computing lies the problem of actively controlling the dynamics of a quantum system.

50 | Quantum Oracle Synthesis with an Application to QRNG
Several prominent quantum computing algorithms—including Grover’s search algorithm and Shor’s algorithm for finding the prime factorization of an integer—employ subcircuits termed ‘oracles’ that embed a specific instance of a mathematical function into a corresponding bijective function that is then realized as a quantum circuit representation.

41 | The Nonequilibrium Cost of Accuracy
Accurate information processing is crucial both in technology and in nature.

39 | Control Systems & Systems Software @ IBM Quantum
The field of quantum computing has rapidly developed around a cloud model, in which users receive a remote handle to a quantum system, compile (transpile) quantum programs (circuits) for the target system, and then remotely invoke an execution on the system from which they then fetch the results of.

40 | Parameter Setting in Quantum Approximate Optimization of Weighted Problems
Quantum Approximate Optimization Algorithm (QAOA) is a leading candidate algorithm for solving combinatorial optimization problems on quantum computers.

38 | Pulse-based Variational Quantum Eigensolver and Pulse-Efficient Transpilation
State-of-the-art noisy digital quantum computers can only execute short-depth quantum circuits.

37 | Elevating Quantum Compiler Performance through Enhanced Awareness in the Compilation Stages
Quantum compiler plays a critical role in practical quantum compilation, particularly in the Noise-Intermediate-Scale-Quantum (NISQ) era.

36 | Hybrid Quantum-Classical Machine Learning with Applications
The development of machine learning (ML) and quantum computing (QC) hardware has generated a lot of interest in creating quantum machine learning (QML) applications.

35 | Hybrid Quantum-Classic Computing for Future Network Optimization
Benefited from the technology development of controlling quantum particles and constructing quantum hardware, quantum computation has attracted more and more attention in recent years.

34 | Optimize Quantum Learning on Near-Term Noisy Quantum Computers
In recent years, there has been a significant breakthrough in the development of superconducting quantum computers, with IBM’s 433-qubit quantum computer being a prime example of the progress made in addressing scalability issues.
33 | Quantum Graphical Calculi: Tutorial and Applications
Quantum computing and quantum communication provide potential speed-up and enhanced security compared with their classical counterparts.

32 | Hoare logic for verification of quantum programs
Quantum computing and quantum communication provide potential speed-up and enhanced security compared with their classical counterparts.

31 | Quantum Computing and Quantum Communication in the Financial World
Finance has been identified as the first industry sector to benefit from quantum computing, due to its abundance of use cases with exponential complexity and the fact that, in finance, time is of the essence, which makes the case for solutions to be computed with high accuracy in real time.

30 | Efficient Hamiltonian Reduction for Scalable Quantum Computing on Clique Cover/Graph Coloring Problems in SatCom
Clique cover and graph coloring are complementary problems which have many applications in wireless communications, especially in satellite communications (SatCom).

29 | Rethinking Most-significant Digit-first Arithmetic for Quantum Computing in NISQ Era
In recent years, quantum computers have attracted extensive research interest due to their potential capability of solving problems which are not easily solvable using classical computers.

28 | Pulse Control for Superconducting Quantum Computers
In superconducting quantum computer, quantum gates are compiled down to a sequence of microwave pulses.

26 | Abstractions Are Bridges Toward Quantum Programming
In this talk, I present abstractions that help classical developers reason about the quantum world, with the goal of designing expressive and sound tools for quantum programming.
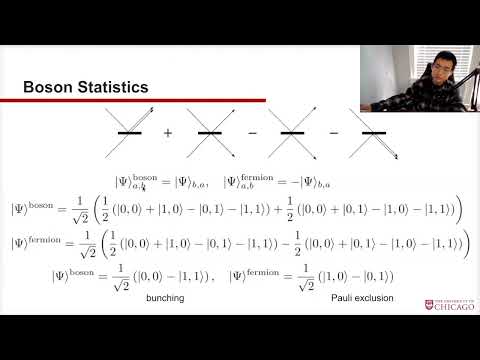
27 | Understanding Quantum Supremacy Conditions for Gaussian Boson Sampling with High Performance Computing
Recent quantum supremacy experiments demonstrated with boson sampling garnered significant attention, while efforts to perfect approximate classical simulation techniques challenge supremacy claims on different fronts.

25 | QDiff: Differential Testing for Quantum Software Stacks
Several quantum software stacks (QSS) have been developed in response to rapid hardware advances in quantum computing.

24 | Automatic Formal Verification of the Qiskit Compiler
Quantum compilers are essential in the quantum software stack but are error-prone.

23 | Software Tools for Analog Quantum Computing
Recent experimental results suggest that continuous-time analog quantum simulation would be advantageous over gate-based digital quantum simulation in the Noisy Intermediate-Size Quantum (NISQ) machine era.
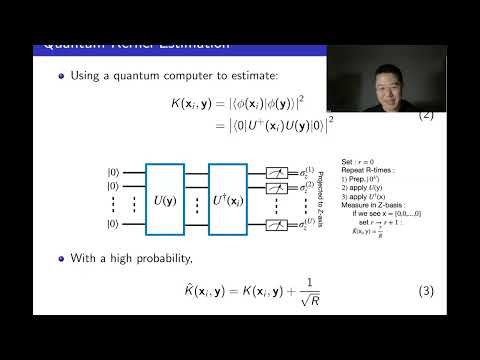
21 | Quantum Machine Learning: Theoretical Foundations and Applications on NISQ Devices
Quantum machine learning (QML) is a trailblazing research subject that integrates quantum computing and machine learning.
22 | Noise Modeling of the IBM Quantum Experience
The influence of noise in quantum dynamics is one of the main factors preventing Noisy Intermediate-Scale Quantum (NISQ) devices from performing useful quantum computations.

20 | Learning and Training in Quantum Environments
Quantum computing presents fascinating new opportunities for various applications, including machine learning, simulation, and optimization.

18 | Enabling Deeper Quantum Compiler Optimization at High Level
A quantum compiler is one essential and critical component in a quantum computing system to deploy and optimize the quantum programs onto the underlying physical quantum hardware platforms.

19 | Classical Verification of Quantum Depth
Verifying if a remote server has sufficient quantum resources to demonstrate quantum advantage is a fascinating question in complexity theory as well as a practical challenge.

17 | Developing Robust System Software Support for Quantum Computers
The field of quantum computing has observed extraordinary advances in the last decade, including the design and engineering of quantum computers with more than a hundred qubits.

16 | Distributed Quantum Computing
Quantum processing units (QPUs) have to satisfy highly demanding quantity and quality requirements on their qubits to produce accurate results for problems at useful scales.

15 | Quantum Crosstalk Robust Quantum Control
The prevalence of quantum crosstalk in current quantum devices poses challenges to achieving high-fidelity quantum logic operations and reliable quantum processing.

14 | Compilation for Near-Term Quantum Computing: Gap Analysis and Optimal Solution
The most challenging stage in compilation for near-term quantum computing is qubit mapping, also called layout synthesis, where qubits in quantum programs are mapped to physical qubits.

13 | Enabling robust quantum computer system by understanding errors from NISQ machines
The growth of the need for quantum computers in many domains such as machine learning, numerical scientific simulation, and finance has urged quantum computers to produce more stable and less error-prone results.

12 | Quantum Computer Hardware Cybersecurity
As Quantum Computer device research continues to advance rapidly, there are also advances at the other levels of the computer system stack that involve these devices.

11 | Building Blocks of Scalable Quantum Information Science
Quantum information technologies are expected to enable transformative technologies with wide-ranging global impact.

10 | Solving Nonlinear Partial Differential Equations using Variational Quantum Algorithms on Noisy Quantum Computers
Partial differential equations (PDEs) have long been the center of interest to system modeling in many disciplines of science and engineering, such as computational physics, fluid mechanics, and quantitative finance.

9 | Protocol Design for Quantum Network Routing
Quantum entanglement enables important computing applications such as quantum key distribution.

8 | Classical Support and Error Mitigation for Variational Quantum Algorithms
In this seminar Dr.

7 | Quantum Data Center
We propose the Quantum Data Center (QDC), an architecture combining Quantum Random Access Memory (QRAM) and quantum networks.

6 | Adaptive Online Learning of Quantum States
Shadow tomography is a fundamental problem in quantum computing, whose goal is to efficiently learn an unknown d-dimensional quantum state using projective measurements.

4 | Enabling Parallel Circuit Execution on NISQ Hardware
Today’s quantum computers are in the Noisy Intermediate-Scale Quantum era and prone to errors.

5 | Design Automation and Software Tools for Quantum Computing
Quantum computing is becoming a reality, but automated methods and software tools for this technology are just beginning.